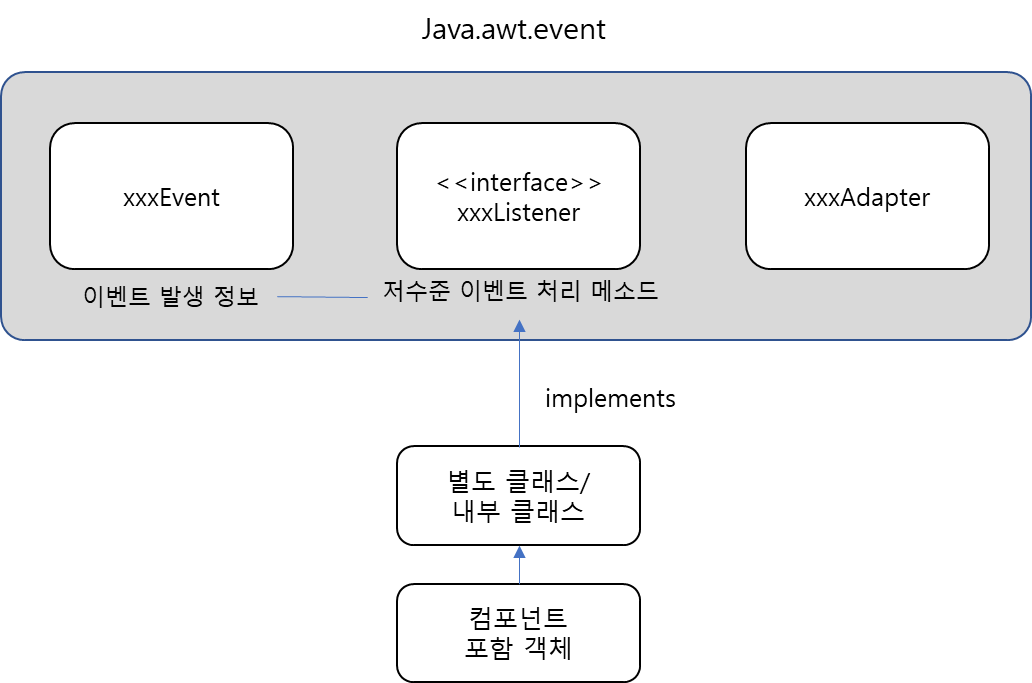
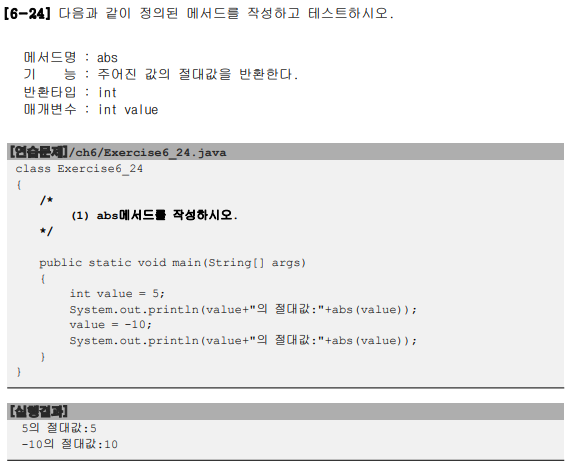
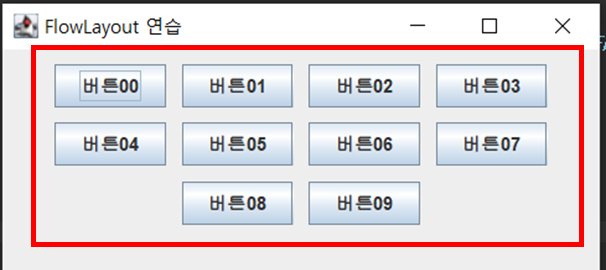
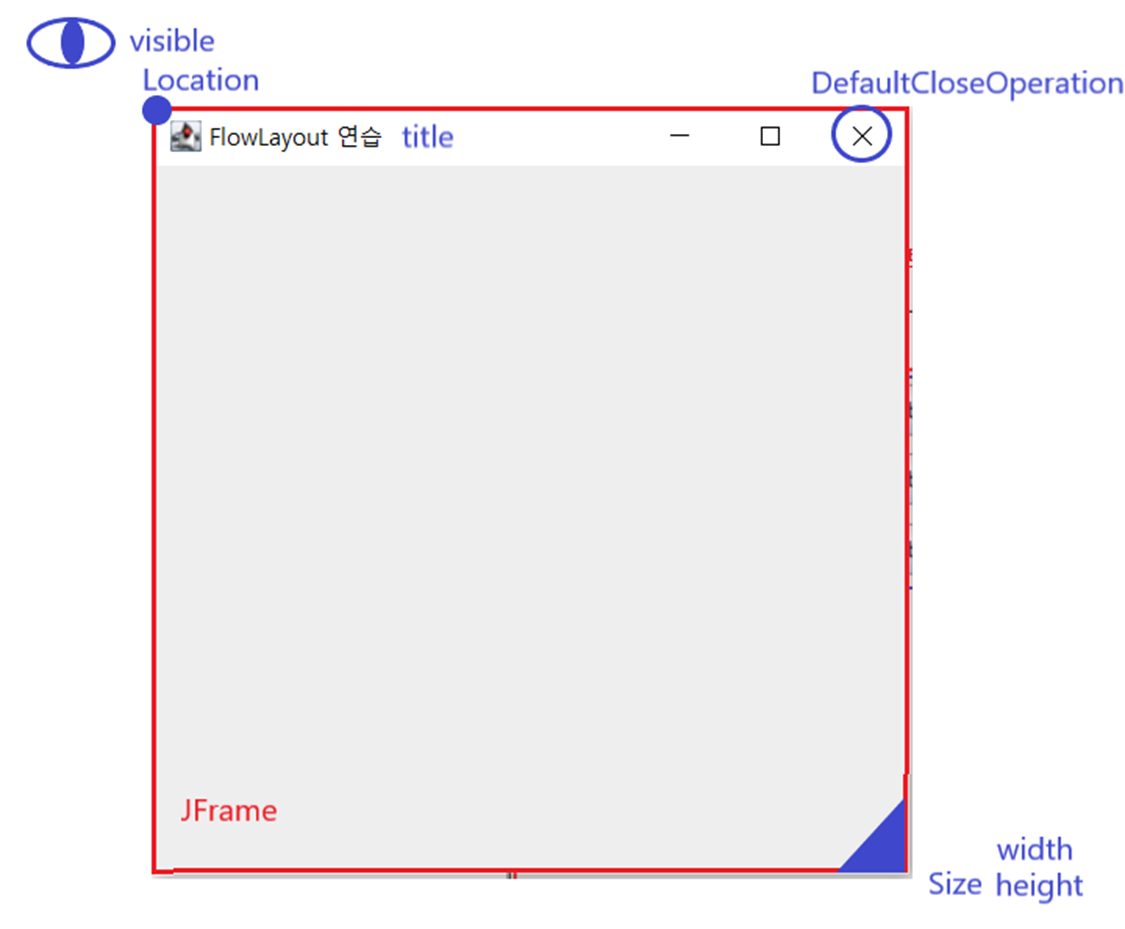
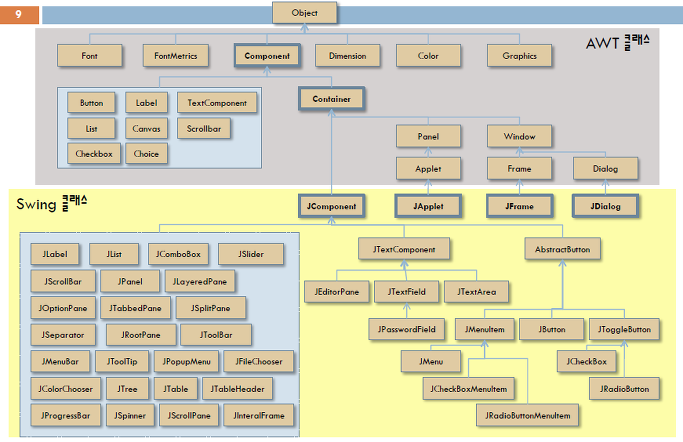
■ 사용할 객체
▶ KeyAdaptor
- KeyListener를 구현한 추상클래스이다.
- getKeyCode() : void ---- Virtual Code를 확인할 수 있다.
| [참고 : 키보드 정보가 들어오는 방식] - 각 회사의 키보드 -> OS/JVM에서 Virtual Key Code로 받음(각 회사 키보드 동일하게 인식) - 키보드의 shift+[ ] 예를 들어, 소문자 a를 인식하는 게 아니다. (문자는 모두 대문자로 인식) - 말그대로 어떤 키보드를 눌렀는지를 값으로 받는다. |
▶ KeyEvent
- VK_xxxxx : Virtual Code Key를 의미하는 상수로, 언더바(_) 다음에 "LEFT","RIGHT","Q","R"등 키보드 키에 대한 상수를 받을 수 있다.
▶ Dimension
- Dimension객체 생성 후, 인스턴스 변수 width/height를 통해 현재 사용하는 컴퓨터의 화면 해상도 얻기
▶ Toolkit
- Dimension객체를 생성할 때 사용할 클래스다.
- Toolkit : 자원(이미지등) 정보 구하는 객체
- getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize() : 툴키트 안의 해상도 사이즈를 구하는 메소드이다.
▶ Point
- (x,y)좌표를 입력할 수 있는 객체이다.
■ 키보드 좌(<-)/우(->)/상/하를 누를 때 윈도우창 이동시키기 (단, 모니터 화면 밖으로 나갈 수 없다.)
package window;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.HeadlessException;
import java.awt.Point;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class MoveExceptMonitor extends JFrame{
int screen_w,screen_h; //모니터 화면 해상도 크기
public MoveExceptMonitor() throws HeadlessException {
super("KeyEvent 연습");
this.setSize(400,400);
this.setLocation(200,200);
this.setVisible(true);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
//화면 해상도 구하기
Dimension d = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
screen_w = d.width;
screen_h = d.height;
//키보드초기화
//키보드 입력시 이벤트를 어떻게 발생시킬 것인지 작성
init_key_event();
}
private void init_key_event() {
KeyAdapter adapter = new KeyAdapter() {
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
//눌린 키 정보 얻어보기
int key = e.getKeyCode();
//현재 윈도우의 위치
//Point pt = MoveExceptMonitor.this.getLocation();
Point pt = getLocation();
//현재 객체의 너비/높이
int sizeWidth = getWidth(); //JDK가 알아서 외부클래스로 인식한다.
int sizeHeight = getHeight();
if(key==KeyEvent.VK_LEFT) {
pt.x = pt.x - 10;
if(pt.x < 0) {
pt.x = 0;
}
}else if(key==KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT) {
pt.x = pt.x + 10;
if(pt.x+sizeWidth > screen_w) {
pt.x = screen_w - sizeWidth;
}
}else if(key==KeyEvent.VK_UP) {
pt.y = pt.y - 10;
if(pt.y < 0) {
pt.y = 0;
}
}else if(key==KeyEvent.VK_DOWN) {
pt.y = pt.y + 10;
if(pt.y+sizeHeight > screen_h) {
pt.y = screen_h - sizeHeight;
}
}
//바뀐 포인트 값으로 윈도우 위치 이동
setLocation(pt.x,pt.y);
}
};
this.addKeyListener(adapter);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MoveExceptMonitor();
}
}'Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바_예제] 2차원 배열 _ 달팽이(snail) 배열 (0) | 2022.03.28 |
|---|---|
| [자바_예제] 2차원 배열_로또 추첨 (0) | 2022.03.28 |
| [자바API_AWT/Swing] 버튼 이벤트 구현하기 (0) | 2022.03.28 |
| [자바API_AWT/Swing] 배치관리자와 레이아웃 종류(2)_윈도우창(JFrame) 예제 (0) | 2022.03.27 |
| [자바의정석_예제] 객체지향프로그래밍1 (0) | 2022.03.27 |